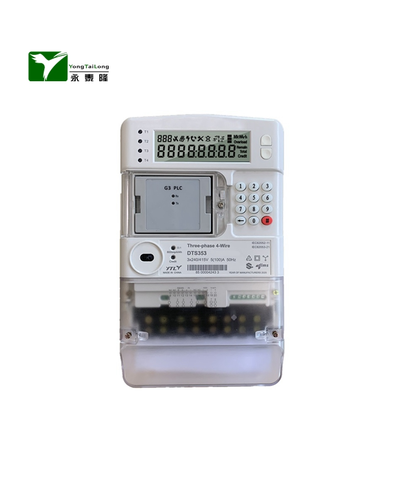
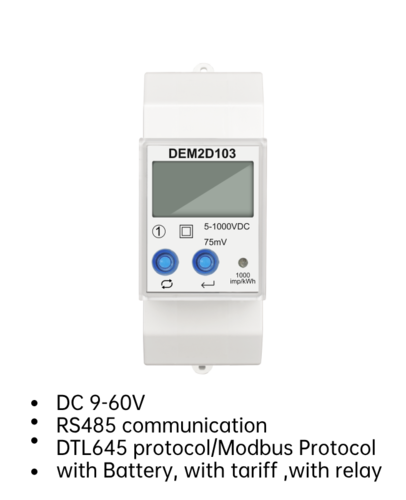
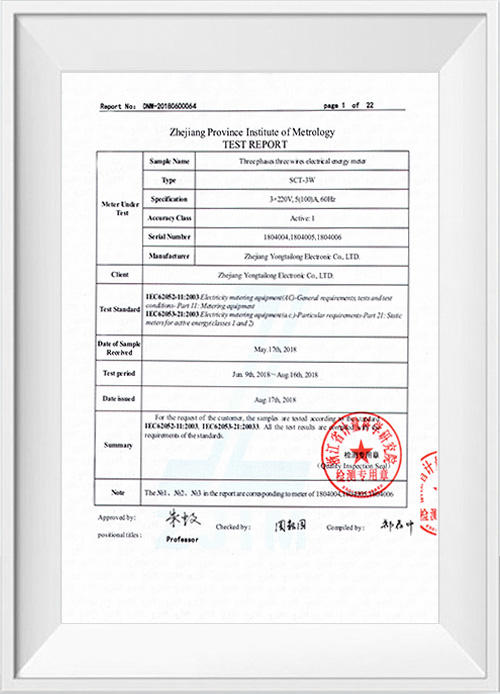
A three phase electronic energy meter is an electronic device that measures the amount of electrical energy consumed by a three phase electrical system. It calculates the active energy (in kilowatt-hours) consumed by a consumer and provides this information to the electricity supplier for billing purposes.
1.Accurate measurement: Three phase energy meters accurately measure the amount of electrical energy consumed by a load.
2.Compatibility: They are designed to work with three phase power supply systems.
3.Multi-functionality: They usually have multiple functions such as measuring voltage, current, power, power factor, and frequency.
4.Digital display: Most modern three phase energy meters have digital displays that show the readings.
5.Communication capabilities: Many energy meters have communication capabilities, such as RS-485, Modbus, or M-bus, for remote monitoring and data logging.
6.Tamper protection: They are equipped with tamper protection features to prevent unauthorized access to the meter.
7.Compact design: Three phase energy meters are compact in size, making them easy to install and integrate into various systems.
8.Durability: They are made to withstand harsh industrial environments and are designed for long-term use.
Advantages and Applications of Three-Phase Electronic Energy Meters
Three-phase electronic energy meters offer several advantages over traditional electromechanical meters. Here are some of their advantages and applications:
Advantages:
1. Accuracy: Electronic energy meters provide higher accuracy compared to electromechanical meters. They use advanced measurement techniques and digital signal processing to achieve precise measurements of active and reactive power, voltage, current, and power factor.
2. Wide dynamic range: Electronic energy meters have a wide dynamic range, allowing them to accurately measure a broad range of power levels, from low to high. This makes them suitable for various applications, including residential, commercial, and industrial settings.
3. Tamper detection: Electronic energy meters can detect tampering attempts such as meter bypass or reverse energy flow. They have built-in features like reverse power detection, phase sequence detection, and load profile monitoring, which help identify unauthorized activities and ensure the integrity of energy measurement.
4. Data logging and communication: Electronic energy meters often come with data logging capabilities, allowing them to record energy consumption patterns over time. They can also communicate with external systems, such as utility management software or smart grid infrastructure, enabling remote monitoring, billing, and load management.
5. Load analysis and power quality monitoring: These meters can provide detailed information about energy consumption patterns, load profiles, and power quality parameters. By analyzing this data, users can identify peak demand periods, optimize energy usage, and diagnose power quality issues such as harmonics or voltage fluctuations.
Applications:
1. Residential energy monitoring: Three-phase electronic energy meters are used in residential complexes or multi-tenant buildings to monitor and bill energy consumption for individual units. They can provide accurate measurements of each unit's energy usage and enable remote monitoring and billing functionalities.
2. Commercial and industrial metering: Electronic energy meters are widely employed in commercial and industrial facilities to measure and manage energy consumption. They are suitable for three-phase systems commonly found in these settings and can handle high power levels accurately. This enables accurate billing, load management, and power quality monitoring in large-scale environments.
3. Renewable energy integration: With the growing adoption of renewable energy sources such as solar or wind power, three-phase electronic energy meters play a crucial role in measuring and monitoring energy generation from these sources. They help track the power generated, consumed, and fed back into the grid, facilitating net metering and feed-in tariff programs.
4. Power distribution and smart grid applications: Electronic energy meters are essential components of smart grid systems. They enable two-way communication between the utility and consumers, facilitating demand response programs, remote disconnect/reconnect functionality, outage detection, and load balancing.
5. Energy management and conservation: By providing detailed energy consumption data and load profiles, three-phase electronic energy meters help users analyze and optimize their energy usage. This information allows businesses and individuals to identify areas of high energy consumption, implement energy-saving measures, and monitor the effectiveness of energy conservation efforts.
Choosing the Right Three-Phase Electronic Energy Meter for Your Business
Choosing the right three-phase electronic energy meter for your business requires careful consideration of several factors. Here are some key points to keep in mind when selecting a meter:
1. Accuracy and Compliance: Ensure that the energy meter you choose meets the accuracy standards and regulatory requirements of your region. Look for meters that are certified by relevant organizations or comply with international standards such as the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) standards.
2. Load Capacity: Assess your business's power requirements and choose an energy meter that can handle the expected load. Consider factors such as peak power demand, power factor, and harmonics. Select a meter with a suitable current rating and voltage range to accurately measure your energy consumption.
3. Communication and Data Management: Determine whether you require advanced communication capabilities for your energy meter. Consider whether you need features such as remote monitoring, data logging, or integration with other systems like smart grid infrastructure or building management systems. Choose a meter with the appropriate communication protocols (e.g., Modbus, M-Bus, Ethernet) to meet your needs.
4. Tamper Detection and Security: If security and tamper detection are important to you, look for meters with robust tamper detection mechanisms. These may include features such as sealable enclosures, anti-tamper sensors, or event logging capabilities. Ensure that the meter provides the necessary security measures to protect against unauthorized access or tampering.
5. Power Quality Monitoring: If monitoring power quality is essential for your business, consider meters that offer comprehensive power quality analysis. Look for features like harmonic analysis, voltage sag/swell detection, power factor measurement, and waveform capture. These capabilities can help you diagnose and address power quality issues effectively.
6. Scalability and Future Needs: Consider your business's future energy monitoring requirements. Will you need to expand your operations, integrate renewable energy sources, or implement demand response programs? Choose a meter that can accommodate future scalability and has the necessary features to meet evolving energy management needs.
7. Budget and Cost-Effectiveness: Evaluate the cost of the energy meter and consider its long-term cost-effectiveness. While it's important to stay within budget, prioritize accuracy, reliability, and functionality over solely focusing on the upfront cost. Look for meters that offer a good balance between features, quality, and affordability.
8. Supplier Support and Warranty: Research the reputation and reliability of the meter manufacturer or supplier. Consider factors such as after-sales support, technical assistance, and warranty terms. It's important to choose a reputable supplier that can provide timely support if issues arise or if you require assistance with meter installation, calibration, or maintenance.


 English
English 中文简体
中文简体
.png?imageView2/2/w/500/h/500/format/png/q/100)