Established in 2000, Zhejiang Yongtailong Electronic Co., Ltd. is located in the center of Shanghai, Hangzhou and Suzhou cities. As a professional China Three Phase kWh Meter Company and Three Phase kWh Smart Meter Manufacturers, YTL designs and produces electronic energy meters which are cost-efficient and ideal for the use in solutions for AMR/AMI at residential as well as industrial applications.YTL was one of the first companies in the domestic market with which had an internal R&D department as well as international sales business. YTL is devoted to develop and design all types of wholesale Three Phase kWh Smart Meter, concentrators and solution applications. At present our export volume makes us a leading company for technology and product export to more than 50 countries throughout the world.
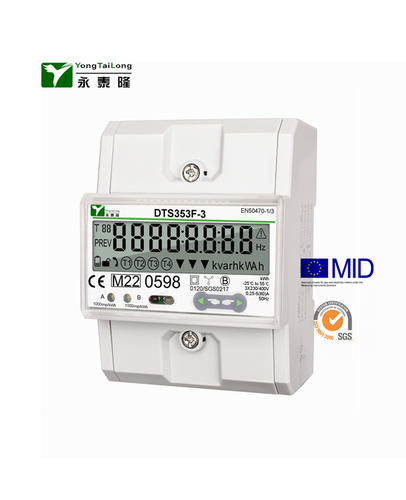
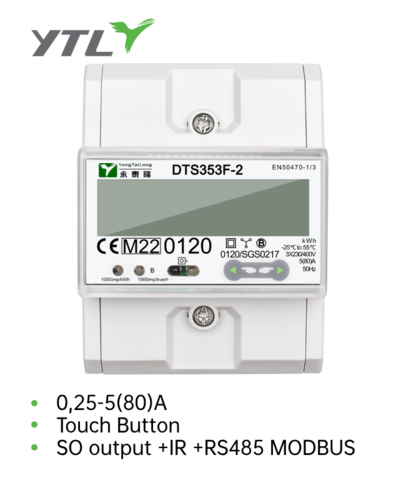
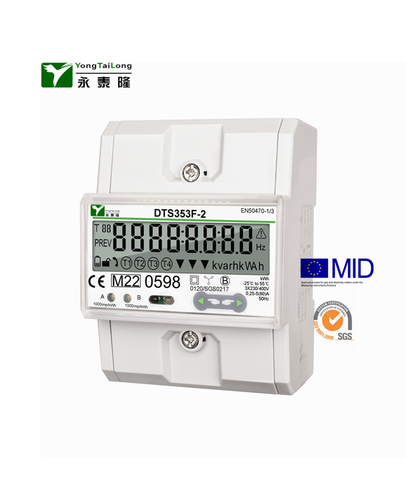
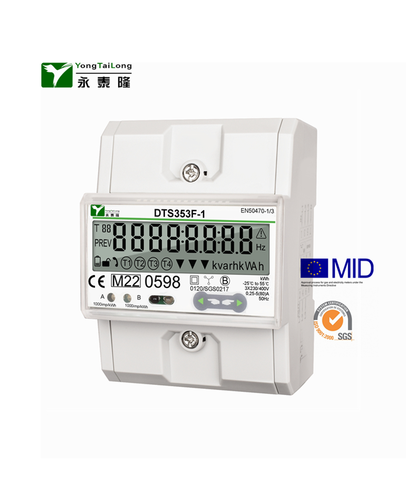
Three Phase kWh Meter Company
YTL metering (Yongtailong) as a professional meter manufacturer in China who has been in this industry for more than 20 years. Our strong ability enable us to well deal with the instability of the lead time which is caused by the shortage of the material shortage all over the world and realize a good increase in the sales .
Welcome To A National High-tech Enterprise
-
2000
Established In
-
500+
Employees
-
50+
Export Country
-
350+
Design Right Patent

YTL News
View All News-
Differences Between DC Meters and AC Meters
2024-10-22DC meters and AC meters have significant differences in several aspects, primarily in the nature of the measured current, working principles, application scenarios, structural characteristics, error c...
-
Why do apartments now like to install smart meters?
2024-10-181. Smart meters have higher measurement accuracy.Compared with traditional meters, smart meters use advanced metering technology and can measure electricity consumption more accurately. This means tha...
-
How smart meters implement load management?
2024-10-12The process of implementing load management with smart meters involves real-time monitoring of users' electricity usage, optimizing electricity usage through data analysis and control strategies, prev...
-
What are the characteristics of building electrical measurement
2024-10-09As an indispensable part of modern building management, building power measurement is characterized in many aspects, including accuracy, real-time, high efficiency and importance for energy conservati...
Industry Knowledge Extension
What is three phase kwh meter?
What are the advantages of three phase kwh meter?
How to calculate kW on a 3-phase meter?
Three-phase electricity refers to a power supply system composed of three alternating potentials with the same frequency, equal amplitude, and phase difference of 120°. In a three phase kilowatt hour meter, each phase can transmit electric energy independently, and the three phases can be balanced with each other to reduce harmonics and imbalance in the power grid.
In a three-phase circuit, kilowatt (kW) is a unit of power, which means the electric energy consumed per unit time. There are generally the following methods to calculate the kilowatt value on a three phase smart energy meter:
1. Direct reading method: Modern three-phase meters usually have a display screen that can directly display the total power (kW) of the three-phase circuit. Users only need to read the value on the display screen.
2. Formula calculation method: If the meter does not directly display the power value, the user can measure the three-phase voltage (U) and the three-phase current (I), and then use the formula P=√3UIcosφ (where φ is the power factor angle) to calculate the kilowatt value. This method requires the user to have certain knowledge of electricity and measurement skills.
3. Integration method: In some cases, in order to obtain a more accurate power value, the integration method can be used for calculation. This method requires the voltage and current measurement values to be integrated, and then the power is calculated based on the integration results. This method is usually used for energy efficiency analysis and optimization of power systems.

 English
English 中文简体
中文简体