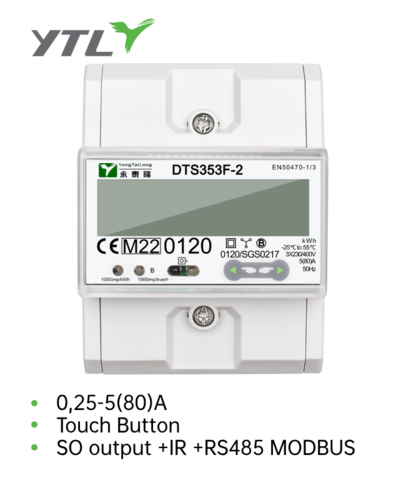
In the precise world of the power system, the energy meter is like a silent judge, but its role varies greatly depending on the application scenario - whether it serves as a legal standard for trade settlement (electricity measurement) or as the data eye for equipment monitoring (electricity measurement), the requirements for the energy meter are vastly different. Selecting a table is essential for precise empowerment!
1、 Core Mission: Legal Authority vs. Technical Insight
Electricity metering (energy meter): a "fair scale" for the economic lifeline
Core objective: To provide legal basis for electricity bill settlement and trade assessment, directly involving the distribution of economic benefits. A 0.1% error is a huge capital deviation in transactions of one million kilowatt hours.

Key requirements:
Legal compliance: In China, electric energy meters must strictly comply with national regulations such as the "Metrology Law" and the "JJG 596 Electronic AC Energy Meter Verification Regulations". Electric energy meters that have not undergone mandatory verification and have been affixed with a qualified verification mark (seal) shall not be used for settlement.
Ultra high precision and long-term stability: Settlement gateway meters often require 0.2S or even 0.1 level accuracy (error ± 0.2% or ± 0.1%), and remain stable within the verification cycle (usually 6-8 years). The requirements for anti-aging and environmental adaptability (temperature and humidity) are strict.
Data cannot be tampered with and can be traced: The electric energy meter adopts legal sealing, and the recorded data has legal effect. The functions of freezing battery life and event recording (lid opening, voltage loss, current loss) are indispensable to ensure complete and traceable data.
Authoritative traceability: The measurement value of the energy meter must be traceable to the national energy standard to ensure fair and unified national settlement.
Electricity measurement (energy meter): a diagnostic tool for optimizing operation
Core objective: To provide real-time and multidimensional data support for energy efficiency analysis, equipment monitoring, fault diagnosis, and power quality governance, with a focus on technical value.
Key requirements:
Functional richness: In addition to active/reactive energy, an electric energy meter needs to accurately measure parameters such as voltage, current, power (active/reactive/apparent), power factor, frequency, harmonics (THD, various contents), voltage fluctuations/flicker, etc.
Dynamic performance and response speed: The electric energy meter quickly captures transient events (such as voltage dips and surges), load fluctuation details, high sampling rate, and strong waveform capture ability.
Data depth and analysis capability: The electric energy meter supports high-density data recording (such as seconds and minutes), trend analysis, alarm triggering, PQ event recording, which facilitates deep diagnosis.
Flexibility and compatibility: The energy meter supports multiple communication protocols (Modbus, DL/T645, MQTT, etc.), making it easy to integrate into SCADA, EMS, or IoT platforms. Flexible installation methods (rails, panels).
2、 Core Differences: Comparison between Hard Indicators and Core Focus Points
Characteristic dimension power measurement (settlement of energy meters) power measurement (monitoring of energy meters) difference core
Does the core mission of trade settlement, legal basis operation monitoring, technical analysis, and energy efficiency management involve "money" and legal effectiveness
Precision Core Electric Energy Accuracy (0.2S, 0.5S, Level 1) Multi functional Accuracy (Voltage, Current, Power, Harmonics, etc.) Measurement: dead end electric energy error; Measurement: Pursuing parameter breadth and dynamic accuracy
Compliance with regulations requires mandatory testing, legal sealing, and strict recommendations for calibration/testing. There are no mandatory legal requirements for measurement: law is the lifeline; Measurement: The standard is the reference line
Data core freezing power, event recording (anti-theft) real-time waveform, trend recording, alarm event measurement: emphasizing settlement basis to prevent tampering; Measurement: Emphasize process analysis and diagnosis
Long term stability is extremely strict (stable within the level for several years), which is important, but allows for some drift (software calibratable). Measurement: stability=money; Measurement: Stability affects analysis accuracy
Function focus core: precise measurement of electrical energy core: multidimensional parameter measurement and advanced analysis measurement: specialized and deep (electrical energy); Measurement: Broad and specialized (multi parameter+analysis)
Typical application scenarios include user billing meters, power generation gateway, inter provincial/inter grid gateway distribution room monitoring, key equipment energy efficiency analysis, PQ diagnosis, microgrid monitoring, data center settlement vs. operation and maintenance
3、 Misplaced selection: a costly misconception
The energy meter is used to measure:
Overqualified and underutilized, high cost: The price of metering grade meters is much higher than that of feature rich meters.
Lack of insight: Lack of deep parameters such as harmonics and power quality, making it difficult to support refined management.
Poor flexibility: Communication protocols and data recording depth may not meet advanced analysis requirements.
Measuring energy meters are used for measuring:
The legal risk is enormous: data issued by measurement meters that have not undergone mandatory verification do not have legal settlement effect. Once disputes arise, enterprises will be put in a passive position.
Accuracy is not guaranteed: The measurement accuracy (such as level 1) and long-term stability of electric energy meters are usually lower than those of measuring meters (such as 0.5S level), and long-term accumulated errors lead to huge economic losses.
Doubtful data reliability: Lack of legal seals and strict event recording mechanisms, data is easily questioned, and the ability to prevent electricity theft is weak.
4、 Intelligent Integration: The Future Path of High end Energy Meters
With the development of technology, high-end intelligent energy meters (such as the DTSD/DSSD series) take into account the advantages of both:
Measurement core: The core measurement unit of the electric energy meter meets the accuracy requirement of 0.5S/0.2S level, and can be used for settlement through mandatory calibration.
Measurement extension: The electric energy meter integrates high-precision power measurement chips, providing rich functions such as full power parameters, harmonic analysis, PQ monitoring, etc.
Dual parallel: The electric energy meter provides reliable legal data for settlement and deep technical insights for operation and maintenance.
Selection suggestion: Clarify core requirements! Regarding settlement, assessment, and legal basis, it is mandatory to select metering energy meters that have passed mandatory verification. If it is for operational analysis, energy efficiency improvement, or fault diagnosis, then a powerful power measurement energy meter is preferred. High end integrated meters are an ideal choice for important assets and key nodes such as large enterprise gateways and new energy power stations.

The value of an electric energy meter is rooted in its role positioning. Confusing the requirements of electricity metering and electricity measurement can result in either wasted investment and inefficient management, or legal risks and significant economic losses. Understanding the essential differences between the two in terms of legality, precision core, functional emphasis, and data requirements is the key to scientific selection, precise investment, ensuring compliance, and unleashing the value of data. Let every electric energy meter, in its position, safeguard the safe, efficient, and compliant operation of the enterprise!

 English
English 简体中文
简体中文








.png?imageView2/2/w/500/h/500/format/png/q/100)





